Abstract
Payment fraud can be defined as an intentional deception or misrepresentation that results in an unauthorized benefit. Fraud schemes are becoming more complex and difficult to identify. It is estimated that industries lose billions of dollars annually because of fraud. The ideal solution is where you avoid making fraudulent payments without slowing down legitimate payments. This solution requires that you adopt a comprehensive fraud business architecture that applies predictive analytics.
Payment fraud is a significant problem for industries, such as banking, property/casualty insurance, and tax revenue. Technological advancements can help you move from a post-payment to pre-payment fraud detection architecture. IBM® System z® supports these advancements as well as providing traditional mainframe benefits. This IBM Redbooks® Solution Guide describes a fraud detection solution on System
z.
Contents
Payment fraud can be defined as an intentional deception or misrepresentation that results in an unauthorized benefit. Fraud schemes are becoming more complex and difficult to identify. It is estimated that industries lose billions of dollars annually because of fraud. The ideal solution is where you avoid making fraudulent payments without slowing down legitimate payments. This solution requires that you adopt a comprehensive fraud business architecture that applies predictive analytics.
Payment fraud is a significant problem for industries, such as banking, property/casualty insurance, and tax revenue. Technological advancements can help you move from a post-payment to pre-payment fraud detection architecture. IBM® System z® supports these advancements as well as providing traditional mainframe benefits. This IBM Redbooks® Solution Guide describes a fraud detection solution on System z.
Figure 1 gives an overview of predictive model processing.

Figure 1. Predictive model processing
Did you know?
To move from post-payment to pre-payment (real-time) detection requires that the detection system is moved closer to the payment system. Until recently, the state-of-the-art solution was to insert an interrupt into the transactional system, which would call the analytic system for a judgment of the transaction. However, latency (delay) is part of the process because of the resources and time that is used moving back and forth from one system to another. Because of this limitation, most payers perform this type of in-line detection on only a small sample of payments. This potentially allows some fraudulent payments through. Another problem is that stale data feeds the models because this solution relies on snapshots of the data.
Two technological advances make real-time and in-transaction pre-payment fraud detection a reality. One is the IBM DB2® Analytics Accelerator (IDAA), which directly links the analytics data with the operational data, significantly increasing the freshness of the data. The other is the IBM SPSS® Modeler 15 Real-time Scoring with DB2 for z/OS®, which allows the scoring of a payment to be made directly within the OLTP system, with only a small latency penalty, versus making calls for scoring at run time to web services.
Business value
Organizations can use real-time scoring to directly incorporate the newest and most relevant data into the decision making process in real time. You can use this scoring to proactively and repeatedly reduce costs and increase productivity. For example, you can complete the following tasks:
Real-time scoring capability on DB2 for z/OS, combined with System z service quality, offers improved accuracy, speed, and performance while reducing the overall cost and complexity. The timeliness of real-time scoring increases efficiency and reliability; also, it is easily implemented.
Solution overview
This solution uses IBM SPSS Modeler Client to develop a modeler stream that is based on a business scenario and requirements. For example, a model can be developed for credit card fraud detection that can predict the probability of a credit card transaction being fraudulent. This model references historical data and predicts a probability score that can be used to decide whether to accept, reject, or keep a transaction on hold. After development, the model is published to the Scoring Adapter for DB2 on z/OS. Then, the model is started with a native SQL call to the user-defined function that returns the predicted score that you can use to make business decisions.
Figure 2 shows this process.
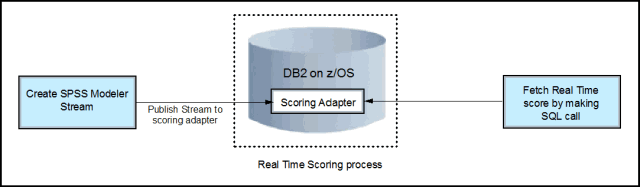
Figure 2. Block diagram of real-time scoring by using the DB2 Scoring adapter
Solution architecture
This solution involves two steps. Step one involves creating a model and publishing it to the scoring adapter on z/OS. This step is rerun only when the model must be changed. In step two, the scoring adapter applies the logic of the model to each incoming transaction in real time.
You use IBM SPSS Modeler Server to add predictive analytics to OLTP applications that are running on z/OS by creating and training the models and then publishing them into DB2 on z/OS. Figure 3 shows a sample SPSS Modeler stream.
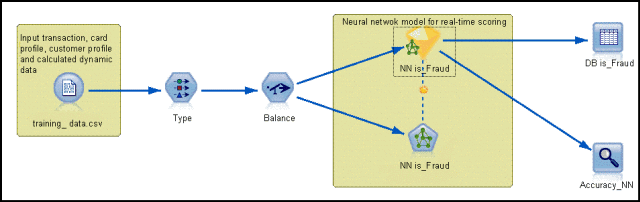
Figure 3. SPSS Modeler stream
The SPSS Modeler Server Scoring Adapter provides a scoring engine that runs in real time. The adapter defines a user-defined function (UDF) that applications can start by using SQL to run the scoring models in-line within their transactions, by using live data as the input for scoring.
After the model is published to the scoring adapter, the process of analyzing each transaction can begin, which is explained in the following list:
A feedback loop is created to complete the analytical cycle, with models that are refined with newly captured information, all of which updates the customer profiles in real time.
Figure 4 provides an overview of this process.
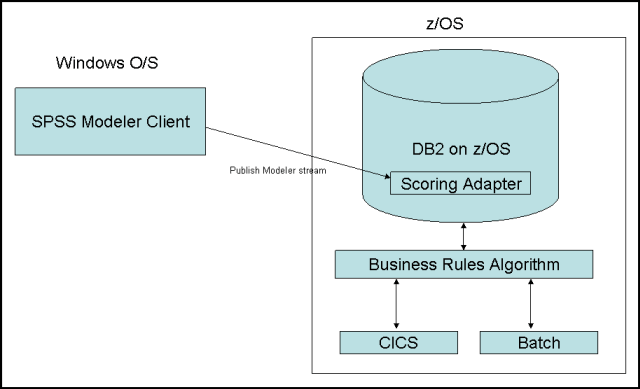
Figure 4. Transactional fraud process in DB2 on System z
Usage scenarios
As an example, picture a customer who is making an online credit card transaction with IBM CICS® as the front end for the transaction.
The customer initiates the transaction to buy something online. He enters his credit card details and continues. After he presses the Enter key, the fraud detection application reads the input data. It starts the UDF that has the scoring adapter by using SQL in DB2. The predictive model uses the information that is provided by the customer. It analyzes the history of the credit card, the previous patterns of the transactions, and other historical data, and then returns the score. A decision-making algorithm reads the score and decides the future course of action. These options include the following ones:
Figure 5 shows an overview of the transactional fraud process in DB2 on System z.
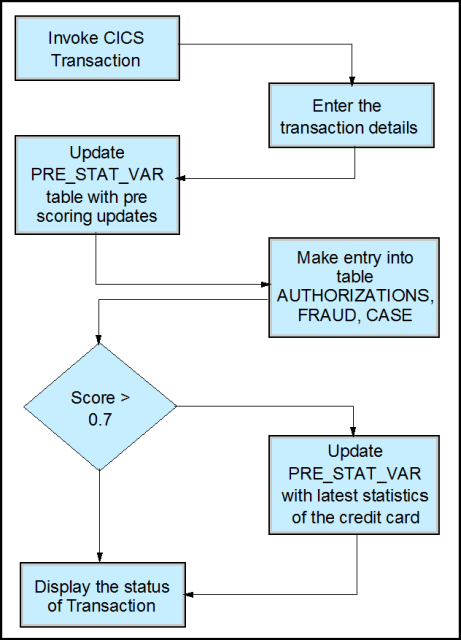
Figure 5. Transactional fraud process in DB2 on System z
Integration
These IBM products comprise the real-time fraud detection solution on System z:
Supported platforms
Ordering information
Ordering information is shown in Table 1.
Table1. Ordering part number and feature code
Related information
For more information, see the following documents:
Payment fraud is a significant problem for industries, such as banking, property/casualty insurance, and tax revenue. Technological advancements can help you move from a post-payment to pre-payment fraud detection architecture. IBM® System z® supports these advancements as well as providing traditional mainframe benefits. This IBM Redbooks® Solution Guide describes a fraud detection solution on System z.
Figure 1 gives an overview of predictive model processing.

Figure 1. Predictive model processing
Did you know?
To move from post-payment to pre-payment (real-time) detection requires that the detection system is moved closer to the payment system. Until recently, the state-of-the-art solution was to insert an interrupt into the transactional system, which would call the analytic system for a judgment of the transaction. However, latency (delay) is part of the process because of the resources and time that is used moving back and forth from one system to another. Because of this limitation, most payers perform this type of in-line detection on only a small sample of payments. This potentially allows some fraudulent payments through. Another problem is that stale data feeds the models because this solution relies on snapshots of the data.
Two technological advances make real-time and in-transaction pre-payment fraud detection a reality. One is the IBM DB2® Analytics Accelerator (IDAA), which directly links the analytics data with the operational data, significantly increasing the freshness of the data. The other is the IBM SPSS® Modeler 15 Real-time Scoring with DB2 for z/OS®, which allows the scoring of a payment to be made directly within the OLTP system, with only a small latency penalty, versus making calls for scoring at run time to web services.
Business value
Organizations can use real-time scoring to directly incorporate the newest and most relevant data into the decision making process in real time. You can use this scoring to proactively and repeatedly reduce costs and increase productivity. For example, you can complete the following tasks:
- Improve fraud identification and prevent disasters by identifying and denying transactions with a high probability of fraud, such as insurance claims, credit card purchases, and immigration.
- Increase revenue per customer ratio by improving marketing campaign success with higher response rates, better cross-up-sell rates, and lower mailing costs.
- Heighten customer retention with more applicable offers.
- Improve customer service with visibility into the current inventory. You can proactively assess and demand requirements to ensure that products are available on demand.
Real-time scoring capability on DB2 for z/OS, combined with System z service quality, offers improved accuracy, speed, and performance while reducing the overall cost and complexity. The timeliness of real-time scoring increases efficiency and reliability; also, it is easily implemented.
Solution overview
This solution uses IBM SPSS Modeler Client to develop a modeler stream that is based on a business scenario and requirements. For example, a model can be developed for credit card fraud detection that can predict the probability of a credit card transaction being fraudulent. This model references historical data and predicts a probability score that can be used to decide whether to accept, reject, or keep a transaction on hold. After development, the model is published to the Scoring Adapter for DB2 on z/OS. Then, the model is started with a native SQL call to the user-defined function that returns the predicted score that you can use to make business decisions.
Figure 2 shows this process.

Figure 2. Block diagram of real-time scoring by using the DB2 Scoring adapter
Solution architecture
This solution involves two steps. Step one involves creating a model and publishing it to the scoring adapter on z/OS. This step is rerun only when the model must be changed. In step two, the scoring adapter applies the logic of the model to each incoming transaction in real time.
You use IBM SPSS Modeler Server to add predictive analytics to OLTP applications that are running on z/OS by creating and training the models and then publishing them into DB2 on z/OS. Figure 3 shows a sample SPSS Modeler stream.

Figure 3. SPSS Modeler stream
The SPSS Modeler Server Scoring Adapter provides a scoring engine that runs in real time. The adapter defines a user-defined function (UDF) that applications can start by using SQL to run the scoring models in-line within their transactions, by using live data as the input for scoring.
After the model is published to the scoring adapter, the process of analyzing each transaction can begin, which is explained in the following list:
- Gather all data from the appropriate data sources in DB2 for z/OS.
- For the response model, look at all customers in a certain time period who made fraudulent and non-fraudulent transactions, train the data set, and then build patterns and scores.
- The customer-based scores are processed on modeler streams and then published by using the DB2 Scoring Adapter on System z.
- An alert message is displayed on the custom center application. The alert is based on calculated propensity scores and the business rules algorithm, which is developed in COBOL.
A feedback loop is created to complete the analytical cycle, with models that are refined with newly captured information, all of which updates the customer profiles in real time.
Figure 4 provides an overview of this process.

Figure 4. Transactional fraud process in DB2 on System z
Usage scenarios
As an example, picture a customer who is making an online credit card transaction with IBM CICS® as the front end for the transaction.
The customer initiates the transaction to buy something online. He enters his credit card details and continues. After he presses the Enter key, the fraud detection application reads the input data. It starts the UDF that has the scoring adapter by using SQL in DB2. The predictive model uses the information that is provided by the customer. It analyzes the history of the credit card, the previous patterns of the transactions, and other historical data, and then returns the score. A decision-making algorithm reads the score and decides the future course of action. These options include the following ones:
- Successful transaction: The transaction is fine with a low fraud probability. The decision making algorithm identifies a transaction as a good transaction if the score that is returned by the scoring adapter is less than 0.4.
- Transaction on hold: The transaction is doubtful with some probability of fraud. The decision making algorithm identifies this transaction if the score that is returned by the scoring adapter is more than 0.4 and less than 0.7. The application returns a message “Call customer care for more details”.
- Transaction declined: The transaction is a fraud. The decision making algorithm identifies a transaction as fraudulent if the score that is returned by the scoring adapter is more than 0.7.
Figure 5 shows an overview of the transactional fraud process in DB2 on System z.

Figure 5. Transactional fraud process in DB2 on System z
Integration
These IBM products comprise the real-time fraud detection solution on System z:
- IBM zEnterprise®
- IBM IDAA
- IBM z/OS
- IBM CICS
- IBM DB2
- IBM SPSS Modeler Client 15.0 on Windows
- IBM SPSS Data Access Pack V6.1
- IBM SPSS Modeler Client 15.0
- IBM SPSS Modeler 15 Scoring Adapter for DB2 on z/OS
- IBM SPSS Modeler 15 Scoring Adapter for DB2 on z/OS
Supported platforms
- Hardware: IBM zEnterprise
- Software: IBM z/OS and Linux on System z
Ordering information
Ordering information is shown in Table 1.
Table1. Ordering part number and feature code
| Program name | PID number | Charge unit description |
| IBM SPSS Modeler with Scoring Adapter for zEnterprise V15.0 | 5655-AA6 |
Related information
For more information, see the following documents:
- Real-time Fraud Detection Analytics on IBM System z, SG24-8066
http://www.redbooks.ibm.com/abstracts/sg248066.html
- DB2 10 for z/OS Technical Overview, SG24-7892
http://www.redbooks.ibm.com/abstracts/sg247892.html - Using zEnterprise for Smart Analytics: Volume 2 Implementation, SG24-8008
http://www.redbooks.ibm.com/abstracts/sg248008.html
- SPSS Modeler product page
http://www-01.ibm.com/software/analytics/spss/products/modeler/
- IBM Offering Information page (announcement letters and sales manuals) for IBM SPSS Modeler with Scoring Adapter for zEnterprise:
http://ibm.co/185sU22
Others who read this also read
Special Notices
The material included in this document is in DRAFT form and is provided 'as is' without warranty of any kind. IBM is not responsible for the accuracy or completeness of the material, and may update the document at any time. The final, published document may not include any, or all, of the material included herein. Client assumes all risks associated with Client's use of this document.
